Understanding Hearing Aids: Types and Uses for Improved Auditory Health
16 Feb 2024Introduction:
Hearing loss is a common condition affecting millions of people worldwide. Fortunately, advancements in technology have led to the development of hearing aids, devices designed to amplify sound and improve hearing ability. In this article, we will explore the different types of hearing aids available and their various uses in aiding individuals with hearing impairments.
Types of Hearing Aids:
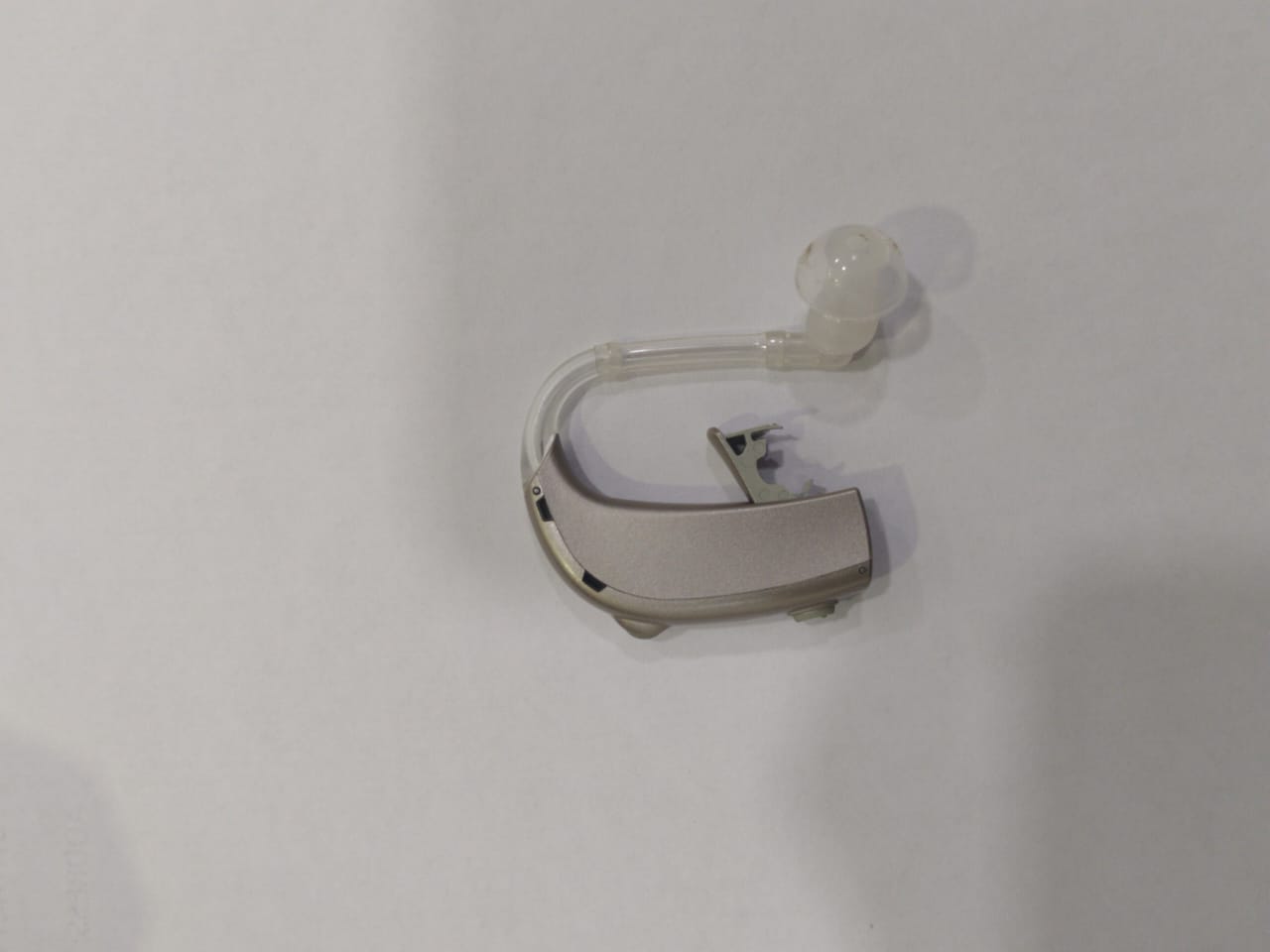
Behind-the-Ear (BTE) Hearing Aids:
BTE hearing aids are among the most common types used today. They consist of a small plastic case that sits behind the ear and is connected to an earmold or tubing that fits inside the ear canal.
These aids are suitable for a wide range of hearing losses and are often preferred for their durability and ease of handling. They can also accommodate additional features like directional microphones and telecoil options.
In-the-Ear (ITE) Hearing Aids:
ITE hearing aids are custom-made to fit the individual's ear canal and are housed in a plastic case that sits in the outer portion of the ear.
These aids are less visible than BTE models and are easier to handle for those with dexterity issues. They are suitable for mild to severe hearing loss.
In-the-Canal (ITC) and Completely-in-Canal (CIC) Hearing Aids:
ITC and CIC hearing aids are custom-made to fit entirely inside the ear canal, making them nearly invisible when worn.
These aids are suitable for mild to moderate hearing loss and offer cosmetic benefits due to their discreet design. However, their small size may limit additional features.
Receiver-in-Canal (RIC) and Receiver-in-the-Ear (RITE) Hearing Aids:
RIC and RITE hearing aids are similar to BTE aids but with the speaker or receiver placed inside the ear canal instead of the main body behind the ear.
This design allows for a more natural sound experience and reduces the occlusion effect (the sensation of hearing one's voice as if it's hollow or booming). They are suitable for mild to severe hearing loss.

Uses of Hearing Aids:
Improved Communication:
Hearing aids amplify sounds, making it easier for individuals with hearing loss to communicate effectively in various settings, including conversations with family and friends, business meetings, and social gatherings.
Enhanced Quality of Life:
By improving auditory perception, hearing aids can enhance an individual's overall quality of life. They enable participation in activities that were previously challenging due to hearing difficulties, such as watching television, listening to music, and enjoying outdoor events.
Safety and Awareness:
Hearing aids help individuals stay alert to environmental sounds, including alarms, sirens, and approaching vehicles, thereby enhancing safety and awareness of their surroundings.
Emotional Well-being:
Untreated hearing loss can lead to feelings of isolation, frustration, and depression. Hearing aids can alleviate these negative emotions by restoring communication abilities and enabling social engagement, thus promoting emotional well-being.
Conclusion:
Hearing aids play a crucial role in improving the quality of life for individuals with hearing loss. With various types available to suit different needs and preferences, they offer effective solutions for enhancing auditory perception and communication abilities. By understanding the types and uses of hearing aids, individuals can make informed decisions to address their hearing needs and regain a sense of connection to the world around them.